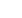
GENERAL
Origin
:
Mediterranean,
sub-tropical,
tropical
Vigour
:
slow-growing
Humidity
:
very arid, semi-
arid, semi-humid
Propagation :
direct sowing,
sowing and
pricking out
Maintenance :
low
CONDITIONS
Urban climate :
resistant
Dessication :
resistant
Stagnant water :
vulnerable
Irrigation
:
none
Salinity/ppm :
moderate (2000
ppm)
Hardiness
:
-3°C
SHAPE
Type
:
shrub
Height
:
0.3 m-1 m
Spread
:
0.6 m-2 m
Foliage
:
deciduous
FLOWER
Colour
:
white, purple
Size
:
5 cm - 7 cm
Period
:
June - August
FRUIT
Type of fruit :
berry
Fruit size
:
3 cm - 5 cm
Toxicity
:
edible when
processed, edible
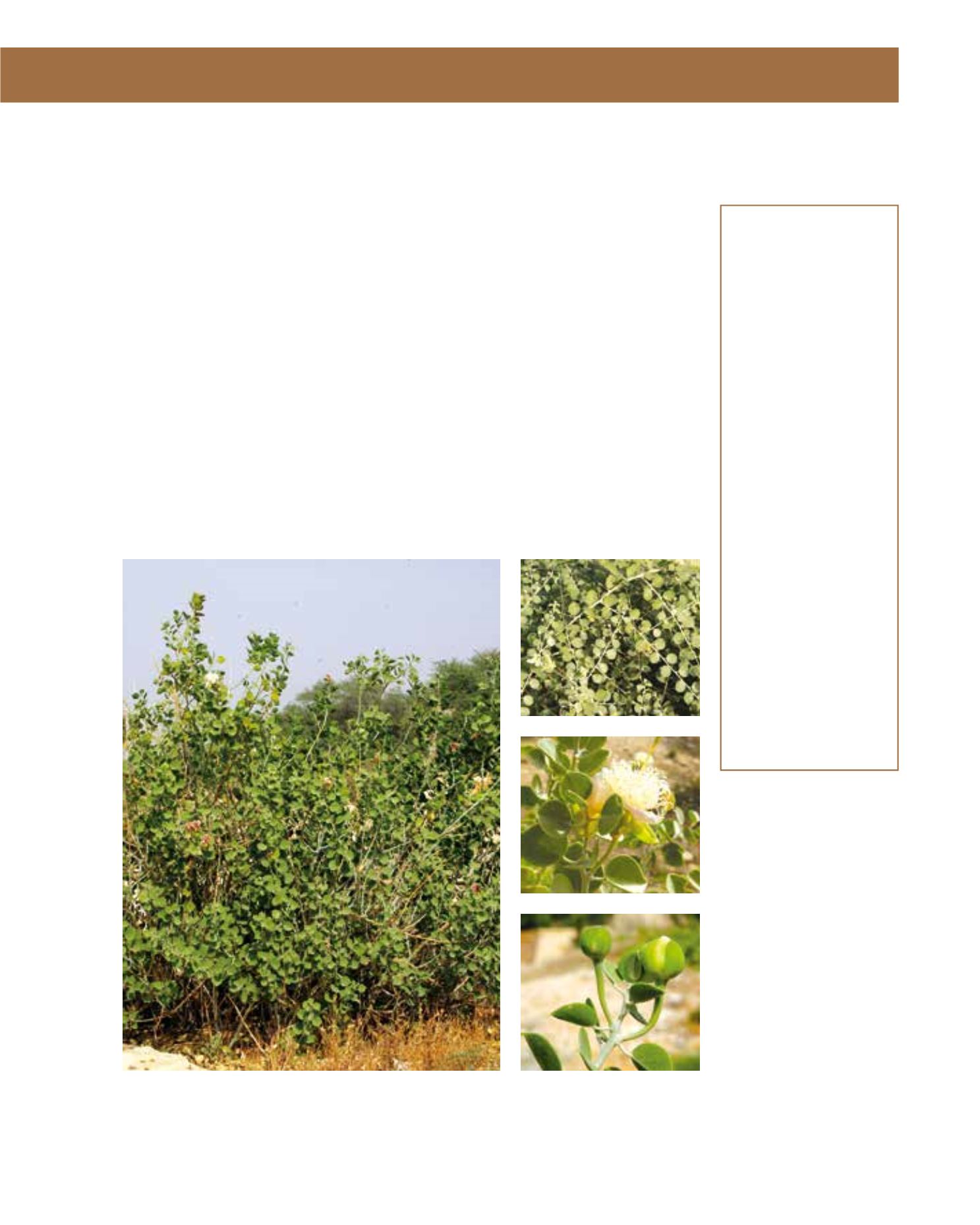
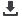
Capparis spinosa has the common Arabic names shaflah, lasaf and malat. The shrub grows slowly
to a height of 1 metre. It can often be seen in Arriyadh, particularly in cracks on the rocky edges
of wadis. The branches with tiny spines in pairs grow from the ground and the 2–4 cm-small lea-
ves are alternate; they have an ovate form and grey-green colour. The flowerbuds can be pickled
to make capers, used in cooking. The beautiful flowers have four petals with stamens almost as
long as the petals. The shrub is propagated by seed and cuttings. Capparis decidua has a number
of common Arabic names including kerda and karir. The generic name is derived from the Arabic
kapar. It is a slow-growing, small tree or shrub reaching a height of 5 metres and thrives on shal-
low, hard soils and stony outcrops. The Capparis is native to arid zones growing on rocky, clayey
and silty soils in Africa, the Middle East and southern Asia. The branches seem to be leafless,
because the leaves are only 2 mm in size. The bark turns silver-grey with time, and tiny spines in
pairs are distributed over the branches. The flowers are bright red and conspicuous, and appear
in small groups in spring and summer. In Africa, the fruits are used for camel fodder, where it is
a very popular and useful plant in agroforestry. C. decidua grows on alkaline, sandy and gravelly
soils. It is well adapted to drought, fire and frost. Both Capparis species are valuable for landscape
design, afforestation and planting for erosion control. Low maintenance requirement.
82
Capparis spinosa,
Capparaceaea
Caper,
lasaf, shaflah